Truthout is a vital news source and a living history of political struggle. If you think our work is valuable, support us with a donation of any size.
Shirley and Don Tillman, residents of Pass Christian, Mississippi, have owned shrimp boats, an oyster boat and many pleasure boats. They spent much time on the Gulf of Mexico before working in BP’s Vessels Of Opportunity (VOO) program looking for and trying to clean up oil.
Don decided to work in the VOO program in order to assist his brother, who was unable to do so due to health problems. Thus, Don worked on the boat and Shirley decided to join him as a deckhand most of the days.
“We love the Gulf, our life is here and so when this oil disaster happened, we wanted to do what we could to help clean it up,” Shirley explained to Truthout.
However, not long after they began working in BP’s response effort in June, what they saw disturbed them. “It didn’t take long for us to understand that something was very, very wrong about this whole thing,” Shirley told Truthout. “So that’s when I started keeping a diary of what we experienced and began taking a lot of pictures. We had to speak up about what we know is being done to our Gulf.”
Shirley logged what they saw and took hundreds of photos. The Tillmans confirm, both with what they logged in writing as well as in photos, what Truthout has reported before: BP has hired out-of-state contractors to use unregistered boats, usually of the Carolina Skiff variety, to spray toxic Corexit dispersants on oil located by VOO workers.
Shirley provided Truthout with key excerpts from the diary she kept of her experiences out on the water with her husband while they worked in the VOO program before they, like most of the other VOO workers in Mississippi, were laid off because the state of Mississippi, along with the US Coast Guard, has declared there is no more “recoverable oil” in their area.
“The first day I went, I noticed a lot of foam on the water,” reads her entry from June 26. “My husband said he had been seeing a lot of it. At that time, we were just looking for ‘Oil.’ We would go out in groups of normally, five boats. The Coast Guard was over the VOO operation. There was always a Coast Guard on at least one of the boats. They would tell us when to leave the harbor, where to go and how fast to go. They had flags on each of the VOO boats and also a transponder. Sometimes we would have one or more National Guardsmen in our group too, as well as an occasional safety man to monitor the air quality and procedures on the boat. If we found anything, the Coast Guard in our group would call it in to ‘Seahorse’ and they would determine what action would be taken.”
Along with giving a clear description of how the Coast Guard was thus always aware of the findings of the VOO workers, her diary provides, at times, heart-wrenching descriptions of what is happening to the marine life and wildlife of the Gulf of Mexico.
“Before we went to work, I went down by the beach,” reads her entry from July 4. “There were dead jellyfish everywhere. Some of them were surrounded by foam. A seagull was by the waters edge, as the foamy stuff continued to wash up. There was also a crane that appeared to be sick. It didn’t look like it had any oil on it, but it just stood there, no matter how close I got.”
On the morning of August 5, Shirley describes spotting a dead young dolphin floating in the water. “As we waited for the VOO Wildlife boat to come pick it up, we noticed a pod of dolphins close by,” she writes. “Even with all the boats around, they did not leave until the dead one was removed from the water. It was very emotional, for all of us.”
It’s a crucial time to fight ignorance – help Truthout get the word out by donating here.
The next day, August 6, found her logging more death. “Last night on the news, they reported a fish kill. Before we went to work, I went to the beach by the harbor. The seagulls were everywhere. As for the dead fish, the only ones on the beach, were ones that the tide had left when it went back out. The rest of the ‘Fish Kill,’ was laying underwater, on the bottom. It was mainly flounder and crab. We only spotted two dead flounder floating that day. I can only imagine how many were on the bottom … I went back to the beach after work. The tide had gone out and the seagulls were eating all the dead fish that had been exposed. You could still see dead fish underwater, still on the bottom. Dead fish don’t float anymore?”
The Tillman’s primary concern is the rampant use of toxic dispersants by what they described as private contractors working in unregistered boats, that regularly were going out into the Gulf as they and other VOO teams were coming in from their days’ work. There was, oftentimes, so much dispersant on top of the water, their boat left a trail.
“The first thing I noticed, was the ‘trail’ the boat was leaving in the water,” her log from July 10 reads. “You could see exactly where we had been, as far back as you could see. Around 11:00, we were in oil sheen and brownish clumps. We were North of Cat and Ship Island when the Coast Guard told us to drop the boom over. When you pick the boom up, you have to wear ‘protective gear.'”
Her log from August 1 describes, in detail, an incident of the Coast Guard not allowing them to collect oil and his proceeding to deny what they found was even oil:
“Around 2:00 p.m., we started noticing a lot of oil sheen. We were North of the East end of Cat Island, but South of the Inter Coastal channel. There was, as usual, a Coast Guard on one of the boats in our team. He called in to report it, but we were told not to drop the boom, it was just ‘Fish Oil.’ In the beginning of the clean-up operation, if something was floating on the water and it looked like oil, it was oil or oil sheen. Later they would sometimes say it was just ‘Fish Oil.’ Also, if it was heavy foam with a brown or rust color, originally it was ‘Oil Mousse.’ Later it was called ‘Algae.’ We were then told to head Northwest. The further we went, the worse the ‘Fish Oil’ got. Then, the foam was mixed in with the oil. It was at least the size of a football field, around our boat alone. My husband got on the radio and asked if they could put the boom over.” The Coast Guard, again, told them no. “We were then headed West, back towards Pass Christian. A pleasure boat flagged one of the boats in our group down and told him that there was oil all over. The Coast Guard said to tell him that they were aware of the situation … On the way back to the Pass Harbor, I asked my husband, ‘Just exactly what are we even doing out here?’ He told me that he was beginning to think that it was all just for show. I can only imagine what the people on the pleasure boat had to say when they got back home that day. Probably, that they had seen a lot of oil on the water and the VOO boats were out there just riding around in it and not doing anything to clean it up. That is exactly what happened. We decided then to start documenting as much as we could. I believe it was the very next day, Thad Allen was on TV saying that they were scaling operations back due to the fact that, ‘No oil has been seen in the Gulf in almost two weeks.’ Now, if we had pulled boom on Sunday and unloaded a bunch of dirty boom in the Pass harbor, it might have been a problem for him later.”
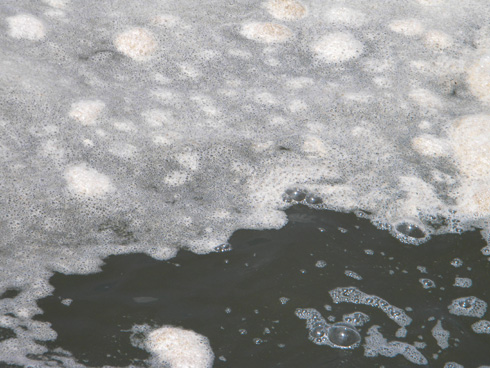
Dispersant remnant, June 26, 2010. (Photo: Shirley Tillman)
On August 5, she describes a rare instance of their being allowed to drop boom in order to collect oil. “We had a Coast Guard and two Safety Men on our boat. We went to the West of the Pass Harbor. The water looked black in places. Lots of bubbles, not foam, just bubbles. Around 8:30, we were in oil sheen and mousse and were told to drop the boom. The more we pulled the boom, it appeared the more was coming up. The Pass [Christian] Harbor was closed because the oil was coming in so bad. We pulled boom back and forth the rest of the afternoon.”

Oiled boom, August 5, 2010. (Photo: Shirley Tillman)

Oil sheen and dispersant remnant, August 1, 2010. (Photo: Shirley Tillman)
By early August, the total number of VOO boats operating out of Pass Christian Harbor, where Shirley and Don worked, was down to 26.
On August 8, Shirley wrote, “talk at the harbor was that airplanes were spraying dispersants on the water at night, out by the islands. There was also talk of skiffs, from Louisiana, with white tanks on them, that were spraying [dispersants] too. We had seen the skiffs before. They would pass us up in the mornings and head towards the Bay St. Louis Bridge. We were told that they were working out of an area at Henderson Point. Henderson Point has a county-owned area with a boat launch & piers. It was closed to the public after the oil spill and a BP sub-contractor staging area was set up. It always appeared that these boats were finishing up their work day, just as we were going to start ours. Most of these skiffs were Carolina Skiffs.”
Later that same morning, Shirley and her husband headed out of the harbor with a member of the National Guard on their boat, heading west, while a member of the Coast Guard and another member of the National Guard were on another boat in their VOO team. After boating for an hour, they turned back to the east, at which point Don spotted five of the Carolina Skiffs.
“I got my camera and started taking pictures of them,” Shirley writes. “As I was zooming in as close as I could, I saw one of them spraying something onto the water. I did not get a picture of it, I was too busy telling my husband to tell the Coast Guard on the other boat. The skiffs had turned North and were scattered out, zigzagging South of the train bridge. The Coast Guard called the incident in and sent one of our boats to follow the skiffs. The skiffs immediately left. When I saw the boat spraying, it was upwind from our boat. Within a few minutes, my nose started drying out. Later my throat and eyes did the same thing. A Coast Guard helicopter was dispatched along with a Coast Guard boat. We saw the helicopter about twenty minutes later, but I never saw the Coast Guard boat.”
Back at Pass Christian Harbor, her team reported the Carolina Skiffs actively spraying dispersants. She was told by the contracting company, Parson’s, that managed their VOO team, to bring in her photographs.
Her entry from the next day, August 9, reads:
“I took the pictures, 8×10’s to Parson’s. A short time later, my husband called and said the Coast Guard wanted me to make a disc of the pictures. I took the disc and turned it over to the Coast Guard. I was told, in the presence of others, that the incident had been investigated and the boats in question had been located at the Henderson Point site. He said that these boats were in the VOO program as skimmer boats, but it had not yet been verified. He said that he had questioned them about spraying something on the water. They told him that if I had seen them spraying anything, they were probably just rinsing out their tanks. He also asked me, ‘Don’t you think if they were spraying dispersants, they would be wearing respirators?’ I told him, ‘You would think so, but nothing surprises me around here anymore.’ We basically left after that. I knew all they had really wanted was to see exactly what I had gotten pictures of. There is of course the question, ‘Why would a skimmer boat need to rinse out his tanks?’ If he had been skimming oil, why dump it back over? If he hadn’t been skimming oil, what was he rinsing out? I know what I saw and I know how I felt afterwards. I also know that in one of the pictures I took, you can see a helicopter over those boats. BP has spotters looking for oil. Could it be he was telling them where to ‘Touch Up’ before they called it a day? One thing I did learn from Coast Guard guy that day, evidently these so-called skimmer boats, also have the ability to spray!”
The Tillman’s curiosity drove them to investigate further, given the inconsistencies they were seeing in the Coast Guard’s actions regarding the dispersant being sprayed from contractors in the Carolina Skiffs.
“My husband came home and said that they had seen the ‘Skiffs’ again today,” reads Shirley’s entry from August 10. “He took pictures of them and a jack-up-rig. The rig moves around in the sound and is suppose to be a de-contamination station. However, some Captains have said when they went there, they were told it wasn’t in operation at the time. After thinking about the tank skiffs and the Coast Guard for two days, I could not make any sense of this whole situation. The Coast Guard is supposedly over the VOO Program, but it knows nothing about the skiffs at the site, so close to the Pass Harbor. They not only tell us every move to make, but they are always with us when we make the moves. Our boats are flagged and have transponders on them. Those boats have no flags, we have not seen a transponder, nor a Coast Guard member on one of them telling them what to do.”
That afternoon, the Tillmans visited the Henderson Point staging area. Though it was guarded, what they found shocked them:
“There were probably more boats there than in the entire Pass [Christian] VOO program at the time,” reads her entry. “There were only a couple of regular skimmer boats. All appeared to have Louisiana registrations. Almost all of the skiffs had the white tanks on them. A few of the tanks looked like they could have had something in them at one time, but nothing like the oily, sticky mess we had been dealing with. If we got something on our boat, it was almost impossible to get it off. I don’t see how they could have gotten it out of the tanks and still looked like they did. Also, there was a Harrison County Sheriffs Department car, right by the boats and some large, plastic, white containers with yellow bases.”

Corner of Canal Road and I-10, in Gulfport, Mississippi, at the Gulfport site used as a BP staging area, August 14, 2010. (Photo: Shirley Tillman)
On August 13, the VOO boat that Shirley and Don were running was deactivated. Still very concerned, the next day they visited the BP staging area in Hancock County.
“They had evacuated this site,” she writes. “Same setup though, a guard and a Sheriff’s car. We then went to a site in Gulfport. Evidently, this is a main BP storage site. There were all kinds of boats, including the tank skiffs. The Sheriffs Department was there also and so was those large, plastic tanks with the yellow bases.”
Other reports, of a very similar nature, have been reported about other BP staging areas along the Gulf of Mexico. The tanks are clearly used to store and transport Corexit dispersant. The Carolina Skiffs are clearly used to spray it atop oil.

Corner of Canal Road and I-10, in Gulfport, at the Gulfport site used as a BP staging area. (Photo: Shirley Tillman)

Corexit tanks, September 1, 2010. (Photo: Shirley Tillman)
Her August 16 entry details her discovery:
“Over the next few days, I continued to go by the Henderson Point site and the Gulfport site. The Henderson Point site brought back a few boats, but none of the tank skiffs or the large plastic tanks. The Gulfport site stayed the same, full of everything. On August 25, I received an email with a link to an article about dispersants. It had a picture of the tanks that dispersants come in, with the label ‘Nalco Corexit EC9005A.’ They were 330 gallon, large, plastic, white tanks with a yellow base. These were the same tanks that I had been seeing at the Henderson Point site and the Gulfport site. I was able to get the name of the manufacturer of the tanks, off a picture I took and compared it to the picture in the article. It was the same manufacturer. I researched this company on the internet and found the 330 gal tanks. They are marketed as: ‘The only manufacturer in the industry to offer portable tanks certified for hazardous goods transport by the United Nations and the U.S. Department of Transportation.'”

Dead flounder among fish kill, August 6, 2010. (Photo: Shirley Tillman)
Shirley and Don are, like tens of thousands of other VOO workers and Gulf residents, left with more questions than answers.
“While working on the boats, if you pull boom back onto the boat, you not only had to wear Tyvek suits, protective glasses and gloves, you also had to put tape around the gloves and suit sleeves, as well as around your boots and the suit.” Shirley asks, “Why would it be safe for people to get into the same water that all of this hazardous stuff was coming out of?”
For the Coast Guard, she aks:
“How can you not know there are boats in the VOO program if you are in charge of the VOO program? The Coast Guard was supposedly over the VOO program, but they acted like they don’t know anything about the Carolina Skiffs. The boats were in either a task force or strike force. Every VOO boat has a flag. We all had transponders. This was VOO and Coast Guard regulations. But these skiffs didn’t have flags and we never saw transponders on them, nor did they have Coast Guard with them and supposedly every group had at least one Coast Guard in each group. Sometimes we would have two. But the Skiffs didn’t have any.”
Local media in Pass Christian and Gulfport, Mississippi, are now reporting that BP hopes to have the VOO program in that area completed by September 19.
Shirley is incredulous. “Why would anyone bring their children here and put them in water that has had millions of gallons of toxic chemicals dumped into it, not counting the oil itself?” she asks. “Why would you want to eat seafood that has been living and dying in the water, with all those contaminates?”
Truthout has earlier reported on other fisherman in the area, James “Catfish” Miller and Mark Stewart, who have reported being eyewitnesses to the contractors in the Carolina Skiffs spraying dispersant as well.
Meanwhile, local, state and federal authorities continue to claim that dispersant was only used south of Mississippi’s barrier islands and that the Carolina Skiffs and the large tanks they carry are only used to “skim” oil.
“If dispersants were only being sprayed South of the islands, why would these 330 gallon hazardous goods tanks be located at two different work sites, right by the tank skiffs?” Shirley asks. “Why would the skiffs tanks be so clean if they were really skimming oil?”
The Tillmans and thousands of other fishermen and residents along the Gulf of Mexico are deeply concerned about local, state and federal government complicity in what they see as a massive cover-up of the oil disaster by using toxic dispersants to sink any and all oil that is located.
Dr. Riki Ott, a toxicologist and marine biologist, is a survivor of the 1989 Exxon Valdez oil disaster in Alaska. She recently submitted an open letter
to the US Environmental Protection Agency expressing many of these same concerns.
Ongoing government denials of this problem neither fool nor dissuade Shirley. “I know what I have seen,” she told Truthout. “I know what I have been told. I know what I have experienced. I know what I have documented. I also know that I have taken hundreds of pictures to verify what I am saying.”
A terrifying moment. We appeal for your support.
In the last weeks, we have witnessed an authoritarian assault on communities in Minnesota and across the nation.
The need for truthful, grassroots reporting is urgent at this cataclysmic historical moment. Yet, Trump-aligned billionaires and other allies have taken over many legacy media outlets — the culmination of a decades-long campaign to place control of the narrative into the hands of the political right.
We refuse to let Trump’s blatant propaganda machine go unchecked. Untethered to corporate ownership or advertisers, Truthout remains fearless in our reporting and our determination to use journalism as a tool for justice.
But we need your help just to fund our basic expenses. Over 80 percent of Truthout’s funding comes from small individual donations from our community of readers, and over a third of our total budget is supported by recurring monthly donors.
Truthout has launched a fundraiser, and we have a goal to add 242 new monthly donors in the next 48 hours. Whether you can make a small monthly donation or a larger one-time gift, Truthout only works with your support.
