Honest, paywall-free news is rare. Please support our boldly independent journalism with a donation of any size.
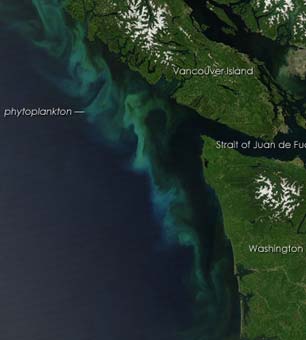
What happens when phytoplankton, the (mostly) single-celled organisms that constitute the very foundation of the marine food web, turn toxic?
Their toxins often concentrate in the shellfish and many other marine species (from zooplankton to baleen whales) that feed on phytoplankton. Recent trailblazing research by a team of scientists aboard the RV Melville shows that ocean acidification will dangerously alter these microscopic plants, which nourish a menagerie of sea creatures and produce up to 60 percent of the earth’s oxygen.
The researchers worked in carbon saturated waters off the West Coast, a living laboratory to study the effects of chemical changes in the ocean brought on by increased atmospheric carbon dioxide. A team of scientists from NOAA’s Fisheries Science Center and Pacific Marine Environmental Lab, along with teams from universities in Maine, Hawaii and Canada focused on the unique “upwelled” zones of California, Oregon and Washington. In these zones, strong winds encourage mixing, which pushes deep, centuries-old CO2 to the ocean surface. Their findings could reveal what oceans of the future will look like. The picture is not rosy.
Scientists already know that ocean acidification, the term used to describe seas soured by high concentrations of carbon, causes problems for organisms that make shells. “What we don’t know is the exact effects ocean acidification will have on marine phytoplankton communities,” says Dr. Bill Cochlan, the biological oceanographer from San Francisco State University oceanographer who was the project’s lead investigator. “Our hypothesis is that ocean acidification will affect the quantity and quality of certain metabolities within the phytoplankton, specifically lipids and essential fatty acids.”
Acidic waters appear to make it harder for phytoplankton to absorb nutrients. Without nutrients they’re more likely to succumb to disease and toxins. Those toxins then concentrate in the zooplankton, shellfish and other marine species that graze on phytoplankton.
Consider the dangerous diatom Pseudo-nitzschia (below). When ingested by humans, toxins from blooms of this single-celled algae can cause permanent short-term memory loss and in some cases death, according to Dr. Vera Trainer, an oceanographer with NOAA’s Fisheries Marine Biotoxins Program. Laboratory studies show that when acidity (or pH) is lowered, Pseudo-nitzschia cells produce more toxin. When RV Melville researchers happened on a large bloom of Pseudo-nitzschia off the coast of Point Sur in California, where pH levels are already low, they were presented with a rare opportunity, explains Trainer, to see if their theory “holds true in the wild.”
Multiple phytoplankton populations became the subjects of deck-board experiments throughout the Melville’s 26-day cruise, which began in mid-May and finished last week.
Another worrisome substance is domoic acid, a neuro-toxin produced by a species of phytoplankton. Washington has a long history of domoic acid outbreaks. The toxin accumulates in mussels and can wind up in humans. “Changes in the future ocean could stimulate the levels of domoic acid in the natural population,” says Professor Charles Trick, a biologist with Western University in Ontario, and one of the RV Melville researchers. Which means that the acidified oceans of tomorrow could nurture larger and more vigorous outbreaks of killer phytoplankton, which could spell death to many marine species.
During their nearly month-long cruise, researchers observed the most intense upwelling in California, which is typical for spring and early summer. Upwelling may increase off the coasts of Oregon and Washington in mid-late summer and fall. The research team took multiple measurements and water samples off all three coasts in waters of both low and high pH. Part of their hypothesis is that concentrations of essential fatty acids are lower when pH is low. They need to establish what exactly “lower'” means, but the bottom line is that fewer essential fatty acids means a less nutritional diet for fish and other organisms.
If the interaction between CO2, ocean acidity and nutrient supply to phytoplankton and other ocean-going creatures isn’t something you can wrap your head around, try this: Every second breath you take is due to phytoplankton. Those single cells generate the lion’s share of the world’s O2. “If they’re out of balance,” says Trainer, “the rest of life on earth is going to be out of balance.”
This article originally appeared on Crosscut.com, an online news organization committed to helping make the Northwest a model for sane and sustainable 21st century living.
Press freedom is under attack
As Trump cracks down on political speech, independent media is increasingly necessary.
Truthout produces reporting you won’t see in the mainstream: journalism from the frontlines of global conflict, interviews with grassroots movement leaders, high-quality legal analysis and more.
Our work is possible thanks to reader support. Help Truthout catalyze change and social justice — make a tax-deductible monthly or one-time donation today.